Students And Quality Assurance Policy In Education
STUDENTS AND QUALITY ASSURANCE POLICY IN EDUCATION
In the era of globalization and active innovation processes, the requirements for human resources in the economy, business, production, and healthcare are constantly changing towards growth.
In this regard, education institutions are faced with the task of ensuring the quality of education, which is the key to success and the main tool for the development of society and all sectoral areas.
Each education institution strives to ensure the quality of education and the acquisition of skills and experience corresponding to the specialty of the educational programme.
2005 by the European Association for Quality Assurance in Higher Education ENQA (European Network for Quality Assurance) were stablished Standards and Guidelines for quality assurance in the European Higher Education Area (ESG / Standards and Guidelines for Quality Assurance in the European Higher Education Area2015)... https://www.enqa.eu/esg-standards-and-guidelines-for-quality-assurance-in-the-european-higher-education-area/
The goal of ESG 2015: to provide an understanding of the principles and approaches in quality assurance of education in all countries all over the world.
Each education institution on the basis of ESG 2015 develops, external and internal Quality Assurance Policy, which includes academic and non-academic quality assurance processes and their relationship.
The quality assurance system is implemented in education institutions with the aim of:
- quality assurance of education and ensuring its sustainability;
- quality assurance of research work and involving students in research to form relevant experience;
- ensuring a high level of satisfaction and expected needs of the core stakeholders (students, faculty, researchers, administration, potential employers of graduates, partnership organizations);
- improving operational efficiency.
The education quality system is assessed through:
- licensing of educational activities,
- post-license control,
- state certification of education institutions,
- certification and audits of the organization's quality management system,
- institutional and specialized (programme) accreditation,
- independent assessment of students' knowledge and skills,
- demand for graduates by employers (employment),
- regular feedback from participants in the educational process, including students,
- certification of specialists
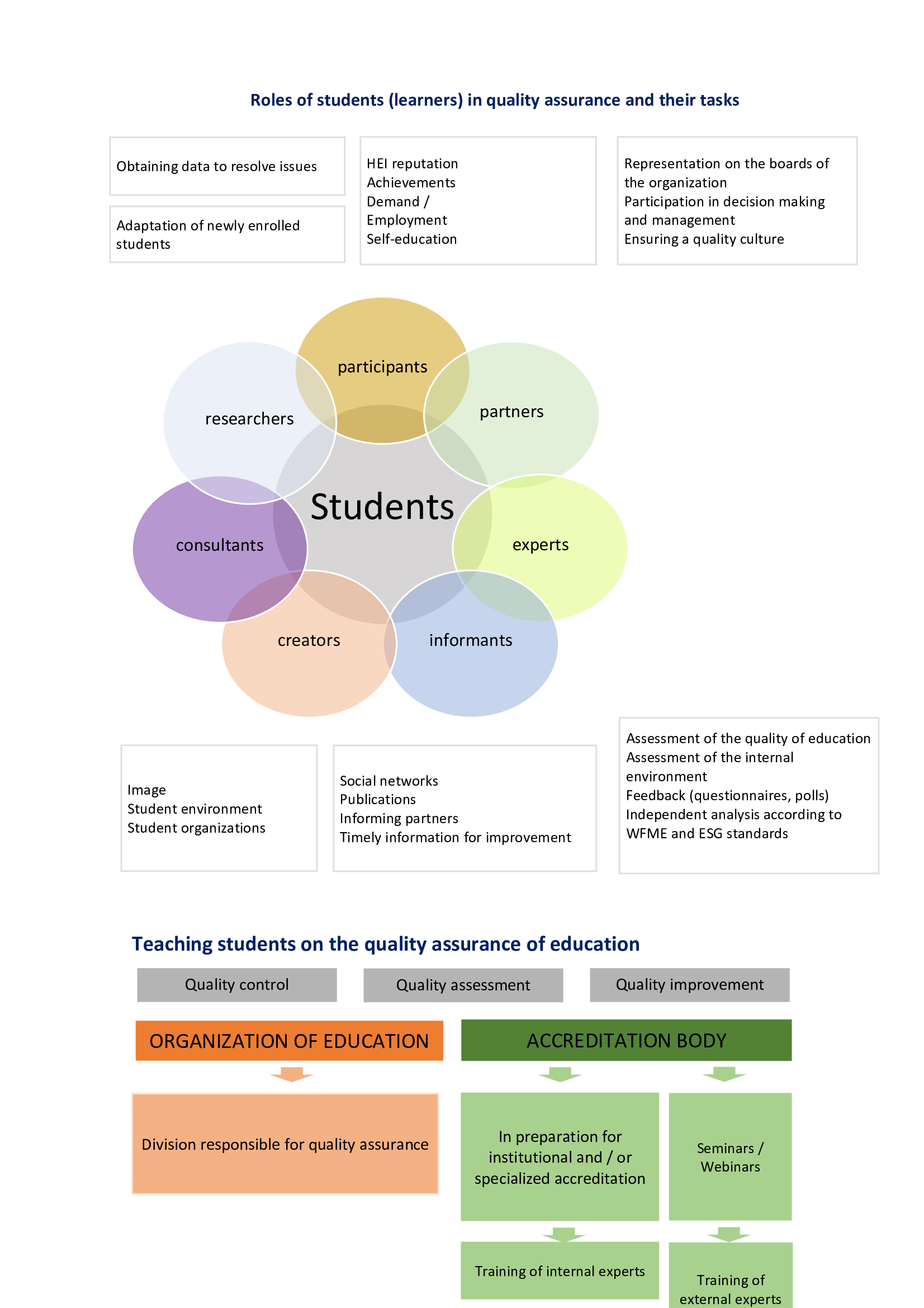
Student regardless of level education is the object and subject of the educational process.
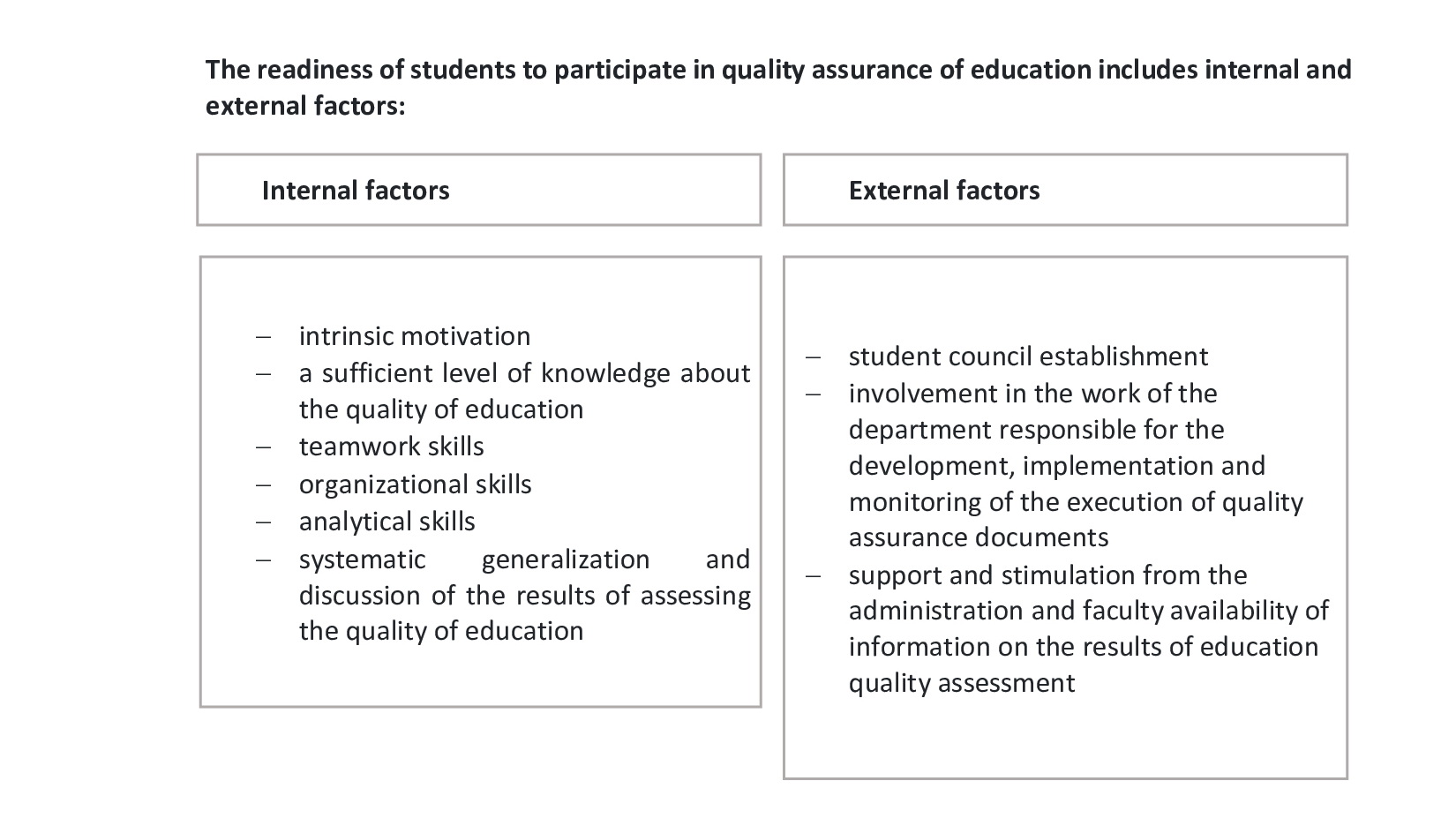
Students participate in quality assurance by providing regular feedback on key issues of the education institution and a specific educational programme, as well as through representation in advisory and advisory bodies responsible for planning, development, approval and monitoring of the educational programme, and participation in strategic events of the education institution.
The objectives for involving learners in the quality assurance process are as follows:
- development of student initiative in the context of quality assurance of education;
- organizing and monitoring the quality of education by conducting questionnaires, surveys;
- a comprehensive assessment of the needs of students as consumers of educational services using various research methods
- attracting students to solving issues of organizing educational process;
- studying the opinions of students to improve educational resources and material and technical base;
- taking into account the educational, scientific, social and professional interests of students;
- providing students with access to the discussion of documents regulating their rights, duties and interests;
- familiarization of students with regulatory legal acts in education;
- informing students about the policy in the field of education quality;
- involving students in assessing the quality of teaching;
- inclusion of students' representatives in educational projects.
Eurasian Centre for Accreditation and Quality Assurance in Education (ECA / ECAQA) developed the Standards for institutional and specialized accreditation of higher education organizations, which are based on ESG 2015 and include 10 Standards
Students participate in the following processes aimed at quality assurance of education:
- development and implementation of a quality assurance policy (1.6)
- compliance with the policy of academic integrity and anti-plagiarism (1.7)
- development of educational programmes (2.8)
- modification of educational programmes based on stakeholder feedback (2.11)
- conducting or participating in small research projects (3.3)
- compliance with the Code of Ethics (3.5)
- regular feedback on teaching and learning methods, assessment methods (3.11)
- student representation and their respective participation in student-related matters (4.8)
- achievement of learning outcomes, academic achievement of students and employment of graduates (7.2)
- feedback for the purpose of assessing the resources (6.12) of the educational process (7.2) by conducting questionnaires, surveys
For Higher Education Institutions of Health Professions Education ECAQA applies the Standards of institutional and specialized accreditation, developed on the basis of the trilogy of International Standards of the World Federation for Medical Education (WFME)
http://www.ecaqa.org/kz/akkreditteu/institutsionaldy-akkreditteudin-standarttary, http://www.ecaqa.org/en/accreditation/standards, http://www.ecaqa.org/akkreditatsiya/standarty-institutsionalnoj-akkreditatsii
As part of the institutional accreditation of Higher Education Institutions of Health Professions Education, students initiate and conduct self-assessment and submit a summary report on independent student analysis which is included in the final self-assessment report.
Key documents describing the role of students in the quality assurance system:
Magna Carta of Universities 1988
- Each university must ensure that the freedom of its students are protected and that appropriate conditions for the acquisition of skills are created that match their interests and needs
Magna Carta of Universities 2020
- The second principle is the continuity of teaching and research with the aim of involving students in the search and deepening of knowledge.
Sorbonne Declaration 1998
- Creation of general provisions for the standardization of the European Higher Education Area and the promotion of student and graduate mobility
Prague Communiqué 2001
- Students must participate in and influence the organization and content of education at universities
Berlin Communiqué 2003
- Student organizations are constructively involved in the Bologna Process
2001 Address of European Rectors (Salamanca)
- Students should be free to choose
Lisbon Declaration of the European Association of Universities "Universities of Europe after 2010", 2007
Higher Education institutions will more and more actively offer diverse educational programmes aimed at acquiring graduates of an expanding range of specialties, including allowing them to move from one higher education institution to another ...
Standards and Guidelines for Quality Assurance in the European Higher Education Area (ESG 2005, 2015).
Educational resources and other mechanisms of the student support system should be freely available to meet the needs of students. Students should be able to express their opinion about the services they provide